3. Stack and Queue
Before diving into graph traversal, we must understand the two key data structures that power them: std::stack (for DFS) and std::queue (for BFS).
3.1 Introduction to std::stack
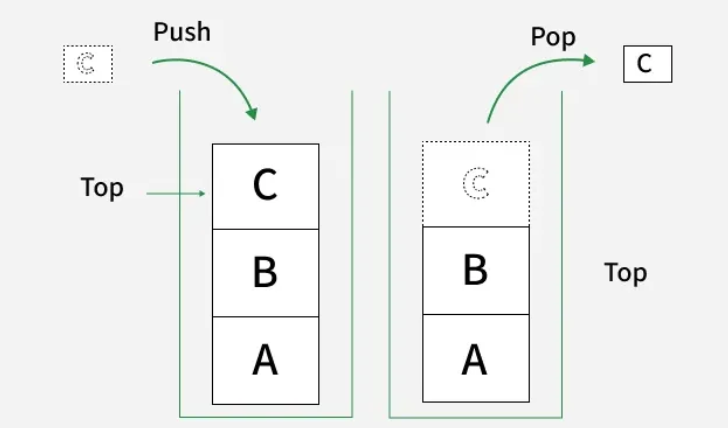
std::stack is a container adapter in the C++ STL. It's not a container itself, but a "wrapper" that provides a specific LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) interface on top of another container (like std::deque by default). It's like a stack of plates. You add new plates to the top and remove plates from the top.
Key Operations:
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
push(item) |
Adds an item to the top of the stack. |
pop() |
Removes the item from the top of the stack. |
top() |
Returns a reference to the item at the top. |
empty() |
Returns true if the stack is empty. |
size() |
Returns the number of items in the stack. |
Example:
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::stack<int> myStack;
myStack.push(10); // Stack: [10]
myStack.push(20); // Stack: [10, 20]
myStack.push(30); // Stack: [10, 20, 30]
std::cout << "Top: " << myStack.top() << std::endl; // Prints 30
myStack.pop(); // Removes 30. Stack: [10, 20]
std::cout << "Top: " << myStack.top() << std::endl; // Prints 20
return 0;
}
3.2 Introduction to std::queue
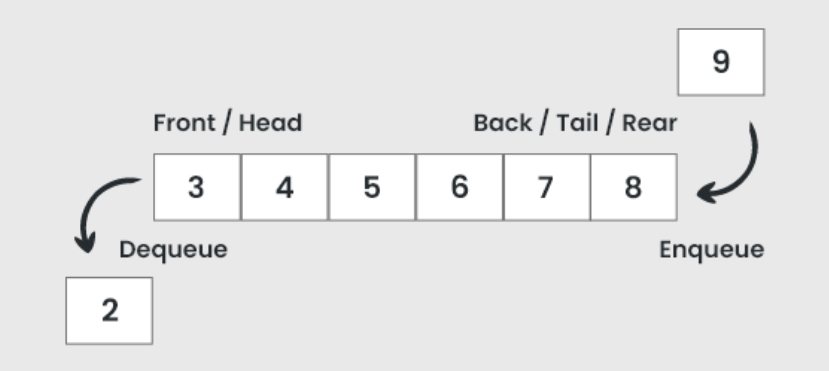
std::queue is also a container adapter. It provides a FIFO (First-In, First-Out) interface. It's like a line at a ticket counter. The first person to get in line is the first person to be served.
Key Operations:
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| push(item) | Adds an item to the back of the queue. |
| pop() | Removes the item from the front of the queue. |
| front() | Returns a reference to the item at the front. |
| back() | Returns a reference to the item at the back. |
| empty() | Returns true if the queue is empty. |
| size() | Returns the number of items in the queue. |
Example:
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::queue<int> myQueue;
myQueue.push(10); // Queue: [10]
myQueue.push(20); // Queue: [10, 20]
myQueue.push(30); // Queue: [10, 20, 30]
std::cout << "Front: " << myQueue.front() << std::endl; // Prints 10
myQueue.pop(); // Removes 10. Queue: [20, 30]
std::cout << "Front: " << myQueue.front() << std::endl; // Prints 20
return 0;
}

No comments to display
No comments to display