Git
What is Git?
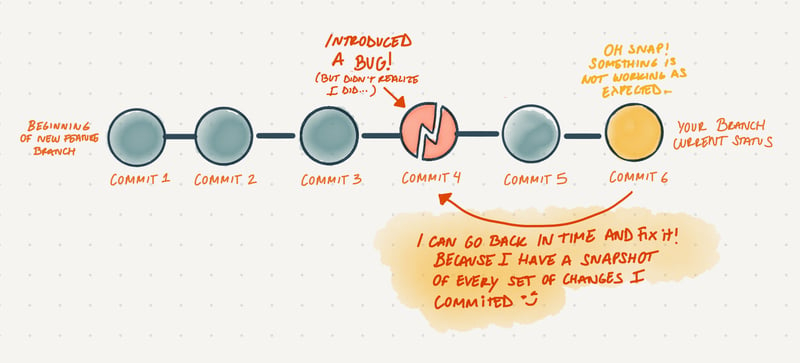
Git is a Version Control System Software. A version control keeps track of every change in your code and it allows you to go back in time when something goes wrong.
Why Use Git?
- Prevents overwriting changes when multiple people work on the same file.
- Keeps a history of changes, making it easy to debug issues.
- Facilitates collaboration with branches and merging.
Git File Status
1. Untracked
-
Files that are not yet being tracked by Git.
-
Example: A new file created in the working directory.
-
Command to Track:
git add <file_name>or
git add .to add all files in the directory.
2. Tracked
- Files that are being tracked by Git, can have three states:
- Unmodified: Files that have not been changed since the last commit.
-
Modified: Files that have been changed since the last commit, this file is needed to be staged with
git addcommand again. - Staged: Files that have been added to the staging area and are ready to be committed.
3. Commited
-
Files that have been saved to the Git database.
-
Command to commit:
git commit -m "Commit message"